(Requires Appendix material)Consider the sample regression function 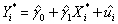 ,
,
where * indicates that the variable has been standardized.What are the units of measurement for the dependent and explanatory variable? Why would you want to transform both variables in this way? Show that the OLS estimator for the intercept equals zero.Next prove that the OLS estimator for the slope in this case is identical to the formula for the least squares estimator where the variables have not been standardized,times the ratio of the sample standard deviation of X and Y,i.e. , 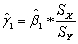 .
.
Definitions:
Short-Run Production
The period in which at least one input or factor of production is fixed, allowing firms to adjust only certain inputs to change output levels.
Average Total Cost
The total cost of production (fixed and variable costs) divided by the total quantity of output produced.
Marginal Cost
The additional cost incurred in the production of one extra unit of a good or service.
Average Fixed Cost
The fixed costs of production divided by the quantity of output produced; these costs decline as production increases.
Q2: Estimation of dynamic multipliers under strict exogeneity
Q5: Experimental effects,such as the Hawthorne effect,<br>A)generally are
Q12: The TSLS estimator is<br>A)(X'X)-1 X'Y<br>B)(X'Z(Z'Z)-1 Z'X)-1 X'Z(Z'Z)-1
Q17: In the simple,one-explanatory variable,errors-in-variables model,the OLS estimator
Q29: The binary variable interaction regression<br>A)can only be
Q33: An example of a quadratic regression model
Q35: A binary variable is often called a<br>A)dummy
Q38: A risk of equity swaps is that
Q38: Your textbook gives the following example of
Q54: An anticipatory hedge is one in which<br>A)the