Economic theory suggests that the law of one price holds.Applying this concept to foreign and domestic goods implies that goods will sell for the same price across countries.The consumer price index is the price for a basket of goods,and is calculated for countries as a whole.Hence in the absence of barriers to trade,and large transportation costs (and the fact that not all goods are traded)you should observe Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)between two countries,or ExchRate × P = Pf,where ExchRate is the foreign exchange rate between the two countries,and P represents the price index,with f indicating the foreign country.Dividing both sides of the equation by the domestic price level then gives you the standard formulation for PPP: ExchRate = 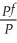 .If PPP holds in the long run,then the exchange rate and the price ratio should share a common trend.Since it is a long-run concept,cointegration provides an interesting way to test for it.
.If PPP holds in the long run,then the exchange rate and the price ratio should share a common trend.Since it is a long-run concept,cointegration provides an interesting way to test for it.
a.Using monthly data for the U.S./U.K.exchange rate ($/₤)and the respective price indexes,you estimate the following regression: 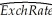 t = 0.44 + 0.69 (lnPUS - lnPUK)
t = 0.44 + 0.69 (lnPUS - lnPUK)
Collecting the residuals from this regression and using an ADF test for cointegration,you find a t-statistic of -2.71.Can you reject the null-hypothesis of no cointegration? What is the critical value?
b.Was it good econometric practice to test for cointegration right away? What else should you have done before proceeding with the EG-ADF test?
Definitions:
Batch-Level Activities
Activities that are performed each time a batch of goods is handled or processed, regardless of how many units are in the batch. The amount of resource consumed depends on the number of batches run rather than on the number of units in the batch.
Unit-Level Activities
Tasks or processes that vary directly with the number of units produced or services provided.
Activity-Based Costing
A costing method that assigns overhead and indirect costs to specific activities based on their use of resources.
Accounting Department
A division within a company that is responsible for managing financial records, ensuring compliance with accounting laws, and preparing financial reports.
Q15: Besides maximum likelihood estimation of the logit
Q17: In a VECM,<br>A)past values of Yt -
Q20: The presence of correlated error terms creates
Q22: Your textbook so far considered variables for
Q28: The conditions for a valid instruments do
Q35: Consider the following two equations to describe
Q44: The kurtosis of a distribution is defined
Q49: In order to calculate the regression R2
Q52: To derive the least squares estimator µY,you
Q53: The candy company that makes M&M's claims