You have collected quarterly data on inflation and unemployment rates for Canada from 1961:III to 1995:IV to estimate a VAR(4)model of the change in the rate of inflation and the unemployment rate.The results are 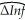 t = 1.02 - .54 ΔInft-1 - .46 ΔInft-2 - .32 ΔInft-2 - .01 ΔInft-4
t = 1.02 - .54 ΔInft-1 - .46 ΔInft-2 - .32 ΔInft-2 - .01 ΔInft-4
.09)(.09)(.09)(.08)(.44)
-.76 Unempt-1 + .20 Unempt-2 - .16 Unempt-3 + .59 Unempt-4
(.43)(.76)(.76)(.44) 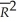 = .26.
= .26. 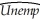 t = 0.18 - .003 ΔInft-1 - .016 ΔInft-2 - .018 ΔInft-3 - .010 ΔInft-4
t = 0.18 - .003 ΔInft-1 - .016 ΔInft-2 - .018 ΔInft-3 - .010 ΔInft-4
(.10)(.016)(.018)(.017)(.016)
+ 1.47 Unempt-1 - .46 Unempt-2 - .08 Unempt-3 + .05 Unempt-4
(.08)(.14)(.14)(.08) 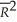 = .980.
= .980.
(a)Explain how you would use the above regressions to conduct one period ahead forecasts.
(b)Should you test for cointegration between the change in the inflation rate and the unemployment rate and,in the case of finding cointegration here,respecify the above model as a VECM?
(c)The Granger causality test yields the following F-statistics: 3.75 for the test that the coefficients on lagged unemployment rate in the change of inflation equation are all zero;and 0.36 for the test that the coefficients on lagged changes in the inflation rate are all zero.Based on these results,does unemployment Granger-cause inflation? Does inflation Granger-cause unemployment?
Definitions:
Dividends In Arrears
Unpaid dividend amounts on cumulative preference shares that must be paid out before any dividends can be distributed to common shareholders.
Paid Preferred Dividends
Dividends distributed to preferred stockholders, typically on a fixed schedule, before any dividends are given to common stockholders.
Declared Preferred Dividends
Dividends announced by a company's board of directors to be paid on preferred shares.
Preemptive Right
A shareholder's right to maintain their proportional ownership in a company by buying a proportionate share of any new stock issues.
Q1: Let W be the included exogenous variables
Q2: The forecast is<br>A)made for some date beyond
Q3: The multiple regression model in matrix form
Q10: An inspector inspects large truckloads of potatoes
Q12: Using the textbook example of 420 California
Q19: Using the California School data set from
Q25: Consider the a model of the U.S.labor
Q38: In a Monte Carlo study,econometricians generate multiple
Q42: The difference between the central limit theorems
Q54: Following Alfred Nobel's will,there are five Nobel