Economic theory suggests that the law of one price holds.Applying this concept to foreign and domestic goods implies that goods will sell for the same price across countries.The consumer price index is the price for a basket of goods,and is calculated for countries as a whole.Hence in the absence of barriers to trade,and large transportation costs (and the fact that not all goods are traded)you should observe Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)between two countries,or ExchRate × P = Pf,where ExchRate is the foreign exchange rate between the two countries,and P represents the price index,with f indicating the foreign country.Dividing both sides of the equation by the domestic price level then gives you the standard formulation for PPP: ExchRate = 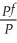 .If PPP holds in the long run,then the exchange rate and the price ratio should share a common trend.Since it is a long-run concept,cointegration provides an interesting way to test for it.
.If PPP holds in the long run,then the exchange rate and the price ratio should share a common trend.Since it is a long-run concept,cointegration provides an interesting way to test for it.
a.Using monthly data for the U.S./U.K.exchange rate ($/₤)and the respective price indexes,you estimate the following regression: 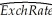 t = 0.44 + 0.69 (lnPUS - lnPUK)
t = 0.44 + 0.69 (lnPUS - lnPUK)
Collecting the residuals from this regression and using an ADF test for cointegration,you find a t-statistic of -2.71.Can you reject the null-hypothesis of no cointegration? What is the critical value?
b.Was it good econometric practice to test for cointegration right away? What else should you have done before proceeding with the EG-ADF test?
Definitions:
Q3: (Requires Appendix material)The following are examples of
Q14: (Continuation from Chapter 4)Sir Francis Galton,a cousin
Q26: The probit model<br>A)is the same as the
Q34: A recent study used umbilical cord blood
Q39: Imagine that you had discovered a relationship
Q46: The accompanying table gives the outcomes and
Q55: A simple random sample of 60 blood
Q61: The following types of statistical inference are
Q82: It is estimated that 780,000 surgical site
Q109: The Poisson distribution is a discrete distribution