You set out to forecast the unemployment rate in the United States (UrateUS),using quarterly data from 1960,first quarter,to 1999,fourth quarter.
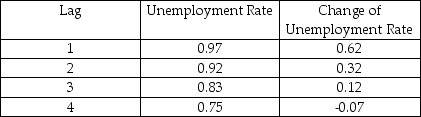
(a)The following table presents the first four autocorrelations for the United States aggregate unemployment rate and its change for the time period 1960 (first quarter)to 1999 (fourth quarter).Explain briefly what these two autocorrelations measure.
First Four Autocorrelations of the U.S.Unemployment Rate and Its Change,
1960:I - 1999:IV
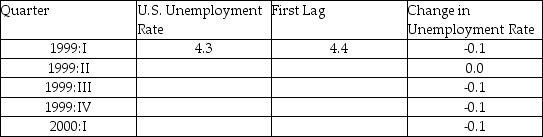
 (b)The accompanying table gives changes in the United States aggregate unemployment rate for the period 1999:I-2000:I and levels of the current and lagged unemployment rates for 1999:I.Fill in the blanks for the missing unemployment rate levels.
(b)The accompanying table gives changes in the United States aggregate unemployment rate for the period 1999:I-2000:I and levels of the current and lagged unemployment rates for 1999:I.Fill in the blanks for the missing unemployment rate levels.
Changes in Unemployment Rates in the United States
First Quarter 1999 to First Quarter 2000
 (c)You decide to estimate an AR(1)in the change in the United States unemployment rate to forecast the aggregate unemployment rate.The result is as follows:
(c)You decide to estimate an AR(1)in the change in the United States unemployment rate to forecast the aggregate unemployment rate.The result is as follows: 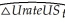 = -0.003 + 0.621 △ UrateUSt-1,R2 = 0.393,SER = 0.255
= -0.003 + 0.621 △ UrateUSt-1,R2 = 0.393,SER = 0.255
(0.022)(0.106)
The AR(1)coefficient for the change in the inflation rate was 0.211 and the regression R2 was 0.04.What does the difference in the results suggest here?
(d)The textbook used the change in the log of the price level to approximate the inflation rate,and then predicted the change in the inflation rate.Why aren't logarithms used here?
(e)If much of the forecast error arises as a result of future error terms dominating the error resulting from estimating the unknown coefficients,then what is your best guess of the RMSFE here?
(f)The actual unemployment rate during the fourth quarter of 1999 is 4.1 percent,and it decreased from the third quarter to the fourth quarter by 0.1 percent.What is your forecast for the unemployment rate level in the first quarter of 1996?
(g)You want to see how sensitive your forecast is to changes in the specification.Given that you have estimated the regression with quarterly data,you consider an AR(4)model.This results in the following output 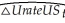 = -0.005 + 0.663 △UrateUSt-1 - 0.082 UrateUSt-2
= -0.005 + 0.663 △UrateUSt-1 - 0.082 UrateUSt-2
(0.022)(0.125)(0.139)
+ 0.106 UrateUSt-3 - 0.176 △ UrateUSt-4 ,R2 = 0.416,SER = 0.253
(0.117)(0.091)
What is your forecast for the unemployment rate level in 2000:I? Compare the forecast error of the AR(4)model with the forecast error of the AR(1)model.
(h)There does not seem to be much difference in the forecast of the unemployment rate level,whether you use the AR(1)or the AR(4).Given the various information criteria and the regression R2 below,which model should you use for forecasting?
p BIC AIC R2
0 0.604 0.624 0.000
1 0.158 0.1181 0.393
2 0.185 0.125 0.397
3 0.217 0.138 0.400
4 0.218 0.1183 0.416
5 0.249 0.130 0.417
6 0.277 0.138 0.420
Definitions:
Human Capital
The competencies, insights, and background that an individual or community has, seen from the perspective of their monetary or value contribution to an entity or state.
Physical Capital
Tangible assets that are used in the production of other goods or services, such as buildings, machinery, and equipment.
Technological Improvements
Innovations and advancements that enhance productivity, efficiency, and product quality in various industries.
Standard Of Living
The level of wealth, comfort, material goods, and necessities available to a person, group, or country.
Q3: The systolic blood pressure of females in
Q13: In practice,the most difficult aspect of feasible
Q15: When a police officer responds to a
Q19: In time series data,it is useful to
Q21: For the United States,there is somewhat conflicting
Q25: (Requires Advanced material)Nonlinear least squares estimators in
Q28: In order to use the t-statistic for
Q29: The OLS estimator for the multiple regression
Q45: Besides the Central Limit Theorem,the other cornerstone
Q46: Are avid readers more likely to wear