Table 7.6
Burdell Industries makes four different models of computer printers: the E-1000,the S-2000,the P-2000 and the N-1000.The E-1000 sells for $200 and has $40 in parts and $40 in labor;the S-2000 sells for $150 and requires $30 in parts and $30 in labor;the P-2000 sells for $100 and has $20 in parts and $20 in labor;and the N-1000 sells for $75 but requires only $10 of parts and $10 of labor.Fixed overhead is estimated at $5,000 per week.The manufacture of each printer requires four machines,Machines #1,2,3 and 4.Each of the machines is available for 40 hours a week and there is no setup time required when shifting from the production of one product to any other.The processing requirements to make one unit of each product are shown in the table.Weekly product demand for the next planning period has been forecasted as follows: 80 E-1000s;65 S-2000s;35 P-2000s;and 20 N-1000s. 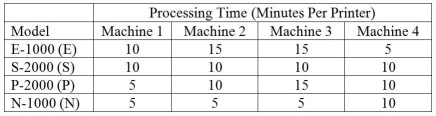 In the questions that follow,the traditional method refers to maximizing the contribution margin per unit for each product,and the bottleneck method refers to maximizing the contribution margin per minute at the bottleneck for each product.
In the questions that follow,the traditional method refers to maximizing the contribution margin per unit for each product,and the bottleneck method refers to maximizing the contribution margin per minute at the bottleneck for each product.
-Use the information in Table 7.6.Using the traditional method,what is the optimal product mix?
Definitions:
Matures
The point in time when a financial instrument, such as a bond or loan, reaches its due date and must be repaid or redeemed.
Accounts Receivable Turnover
A financial ratio indicating how many times a company's receivables are turned over during a specific period, often used to assess the effectiveness of credit and collection policies.
Net Sales
The revenue from the sale of goods or services after deducting returns, allowances, and discounts.
Accounts Receivable Turnover
A financial metric that measures how often a company collects its average accounts receivable balance within a period.
Q32: With a single-server model,increasing the capital-to-labor ratio
Q43: Use the information in Scenario B.4.What is
Q54: Manufacturing an item before it is needed
Q61: A drive-through system at a fast food
Q92: Capacity planning requires a demand forecast for
Q115: In lean systems,work-in-process inventory is a direct
Q137: Products never have more than one defect
Q145: Historically,the average time to service a customer
Q147: Use the information in Table 7.7.Using the
Q149: A bottleneck process has the lowest capacity