Figure Q3-6 is from an experiment that helped show that neurotransmitter release is triggered by presynaptic Ca2+. In panel A, the presynaptic membrane potential was clamped at -25mV. 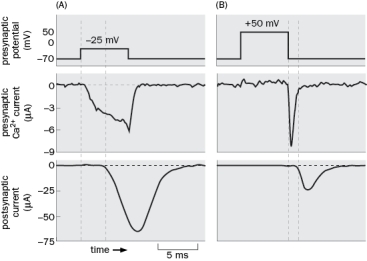 Figure Q3-6
Figure Q3-6
A. How did they know Ca2+ entered the presynaptic neuron?
B. What happened in the postsynaptic neuron?
C. In panel B, the presynaptic membrane potential was clamped at -50mV. Why was there no net current during the presynaptic depolarization?
D. Why was there a current after the presynaptic potential was clamped back to -70mV?
E. What happened to the delay in postsynaptic current with the +50mV presynaptic depolarization?
Definitions:
Synaptic Cleft
The narrow space between the terminal button of a neuron and the dendrite or cell body of another neuron where neurotransmitters are released.
Inhibitory Postsynaptic
Referring to a postsynaptic potential that makes a neuron less likely to generate an action potential, essentially serving to inhibit neuronal firing.
Neuron
A nerve cell that is the basic building block of the nervous system, responsible for receiving and transmitting information through electrical and chemical signals.
Action Potential
A rapid rise and subsequent fall in voltage or electrical charge across a cell's membrane, allowing neurons to transmit signals over distances.
Q9: Which of the following is not true
Q15: SCN neurons are the 'pacemaker cells' for
Q20: Roger Sperry surgically rotated an amphibian's eye,
Q25: Which one of the following is not
Q35: The manager of an appliance store wishes
Q38: A new product should be introduced if
Q45: One way that nociception (the sensation of
Q80: The Ten Critical Decisions of Operations Management
Q100: Henry Ford is noted for his contributions
Q118: A cleaning company uses $10 of chemicals,$40