Figure Q1-14 shows commonly used circuit motifs. Identify the type of circuit motif featured in each of the following examples. 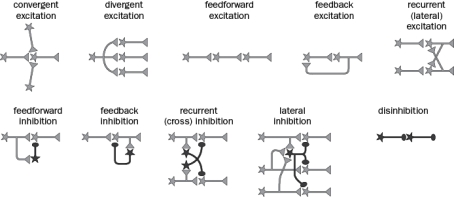 Figure Q1-14
Figure Q1-14
A. In the vertebrate retina, afferent neurons excite inhibitory interneurons that project onto the targets of their neighbors.
B. Sensory neurons relay somatosensory stimuli to the primary somatosensory cortex via nuclei in the brainstem and thalamus.
C. A class of cerebral cortical neurons inhibits other classes of inhibitory neurons in the brain, indirectly increasing the activity of final targets.
D. In the insect olfactory system, excitatory projection neuron axons project to two different brain structures, the mushroom body and the lateral horn.
E. In the vertebrate knee-jerk reflex, two parallel excitatory pathways inhibit each other via inhibitory neuron intermediates.
Definitions:
Material Remains
Physical artifacts or evidence from past human activity, including buildings, tools, and pottery, used in archaeology.
Archaeological Site
Locations where remains of past human activities are preserved and which archaeologists study to understand historical cultures and civilizations.
Paleoanthropology
The anthropological study of biological changes through time (evolution) to understand the origins and predecessors of the present human species.
Human Evolution
The lengthy process of change by which people originated from apelike ancestors, spanning millions of years.
Q9: Which of the following is not true
Q9: Mice that are homozygous mutant for Small
Q9: Which of the following is true of
Q12: Nematocin appears to be a homolog of
Q18: What are 'silent synapses'? Select all that
Q23: Hox genes are highly conserved players in
Q27: Which of the following is true in
Q33: The CASPR/Cas9 system is a new, very
Q35: Suppose the yearly interest rate is given
Q41: It is critical for muscles to contract