The probabilities shown in a table with two rows, 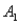 and
and 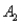 and two columns,
and two columns, 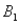 and
and 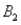 , are as follows: P(
, are as follows: P( 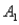 and
and 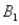 ) = .10, P(
) = .10, P( 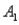 and
and 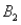 ) = .30, P(
) = .30, P( 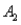 and
and 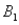 ) = .05, and P(
) = .05, and P( 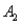 and
and 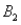 ) = .55. Then P(
) = .55. Then P( 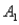 |
| 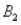 ) , calculated up to two decimals, is:
) , calculated up to two decimals, is:
Definitions:
Real Property
Land and any structures affixed to it, including rights associated with ownership of the land and its buildings.
Prevent Fraud
The set of strategies, actions, or measures implemented to detect, stop, and deter deceptive practices intended to gain unlawful or unfair advantage.
Statute of Frauds
A legal requirement that certain types of contracts must be written and signed by the party against whom enforcement is sought.
Statute of Frauds
A legal principle that requires certain types of contracts to be in writing and signed by the parties involved to be enforceable.
Q18: Correlation and covariance measure:<br>A) the strength of
Q28: A random variable X is normally distributed
Q46: The probabilities shown in a table with
Q57: Perform a simulation assuming the plant will
Q58: Suppose that an highway patrol officer can
Q59: What is Bayes' Rule?<br>A) a rule that
Q60: Which tasks are considered to be marketing
Q73: (A) Is there a significant difference in
Q80: Calculate the mean, variance, and standard deviation
Q113: What is the probability that this company