On January 1, 20X1, Parent Company purchased 8,000 shares of the common stock of Subsidiary Company for $350,000. On this date, Subsidiary had 20,000 shares of $5 par common stock authorized, 10,000 shares issued and outstanding. Other paid-in capital and retained earnings were $150,000 and $200,000 respectively. On January 1, 20X1, any excess of cost over book value is due to a patent, to be amortized over 15 years. Parent Company uses the simple equity method to account for its investment in Sub.
Subsidiary's net income and dividends for two years were: 
On January 1, 20X2, Subsidiary Company sold an additional 2,500 shares of common stock to noncontrolling shareholders for $50 per share.
In the last quarter of 20X2, Subsidiary Company sold goods to Parent Company for $40,000. Subsidiary's usual gross profit on intercompany sales is 40%. On December 31, $7,500 of these goods are still in Parent's ending inventory.
Required:
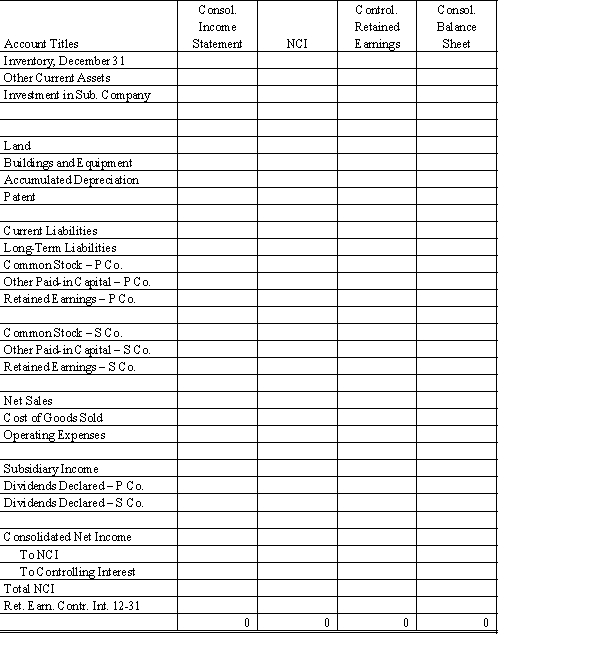
Complete the Figure 8-6 worksheet for consolidated financial statements for 20X2. 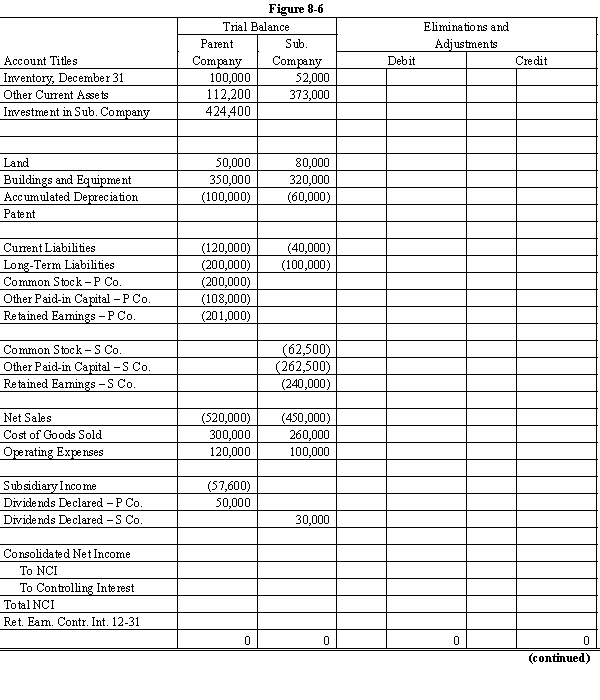
Definitions:
Bully
A person who intimidates or harasses others, typically using strength or influence, to exert control or to demean.
Dyadic Process
A dynamic interaction between two entities or individuals, emphasizing the mutual influence and exchange.
Foot In The Door
A persuasion technique where a small initial request is made to increase the likelihood of compliance with a larger request later.
Lowballing
A sales technique in which a customer is initially offered a lower price than the actual price intended to be charged, after they have agreed to purchase.
Q3: Company P acquired 30% of Company S's
Q3: In order to generate interim financial reports
Q4: On 6/1/X2, an American firm purchased a
Q8: What is infrastructure and where would it
Q9: ACME Co. paid $110,000 for the net
Q11: On July 1, 20X9, the Crawford Company
Q12: Vibe Company purchased the net assets of
Q18: Supernova Company had the following summarized balance
Q21: Under IASB for small and medium entities,
Q29: Rex Corporation, a U.S. firm with a