Stearic acid, nature's most common fatty acid, dimerizes when dissolved in hexane: 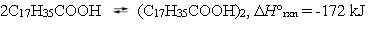 The equilibrium constant for this reaction at 28 C is 2900. Estimate the equilibrium constant at 38 C.
The equilibrium constant for this reaction at 28 C is 2900. Estimate the equilibrium constant at 38 C.
Definitions:
Deactivator
In organic chemistry, a substance that reduces the reactivity of a catalyst or chemical reactant, often by adsorption or by changing its chemical nature.
O,p-director
Substituents in aromatic chemistry that direct incoming substituents to the ortho and para positions on a benzene ring.
Electrophilic Iodination
A chemical reaction involving the addition of an iodine atom to a substrate, typically facilitated by an electrophile.
Major Organic Product
Refers to the main product obtained in the highest yield from an organic reaction, distinguished from any side products or minor products.
Q3: Which relationship or statement best describes
Q15: A cubic unit cell has an edge
Q25: Which of the following elements are the
Q26: Calculate the solubility of silver oxalate, Ag<sub>2</sub>C<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>,
Q38: Write the expressions for K<sub>c</sub> and K<sub>p</sub>
Q52: In nature, some elements exist as molecules,
Q64: Calculate <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\Delta"><span class="katex"><span
Q73: The concentration of iodine in sea water
Q97: A temperature increase causes _ in the
Q100: Consider the equilibrium reaction shown below. B<sub>2</sub>(g)