The bigger the stop sign, the more expensive it is. Here is a graph of the height of a sign in inches versus its cost in dollars.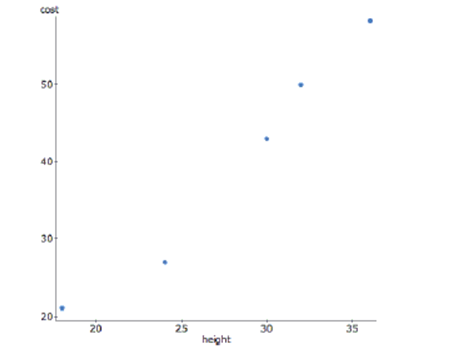
To achieve linearity, the data was transformed using a square root function of cost. Here are the results and a residual plot.
Dependent Variable:
(correlation coefficient)
s: 0.2141
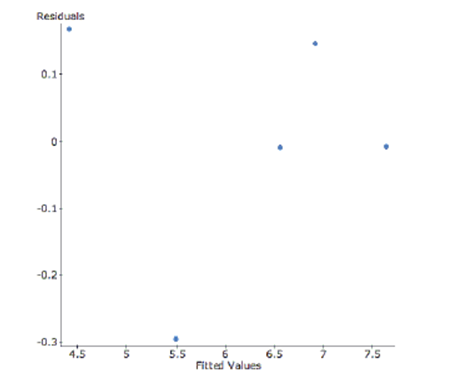
-Interpret R-sq in the context of this problem.
Definitions:
Testing Process
The series of steps or procedures involved in administering, scoring, and interpreting tests or assessments.
Reliability Improvement
Efforts or methods aimed at increasing the consistency and dependability of a process, instrument, or system.
Client's Stress
The level of psychological strain and pressure experienced by an individual seeking professional help or services.
Reliability Estimates
Statistical measures that indicate the consistency of a test's results over time or across different raters.
Q2: In this context describe a Type I
Q31: Surprised by a high number of customers
Q67: What is the probability that if a
Q73: Does Procellera Antimicrobial Wound Dressing help injuries
Q83: Explain clearly whether this data should be
Q84: Test an appropriate hypothesis and state your
Q87: Name and describe the kind of bias
Q96: The blood drive has a total of
Q119: The slope of this model is best
Q718: Compute a 95% confidence interval for the