King Corp. owns 80% of Kong Corp. and uses the cost method to account for its investment, chapter) Corp. for the Year ended December 31, 2012 are shown below: 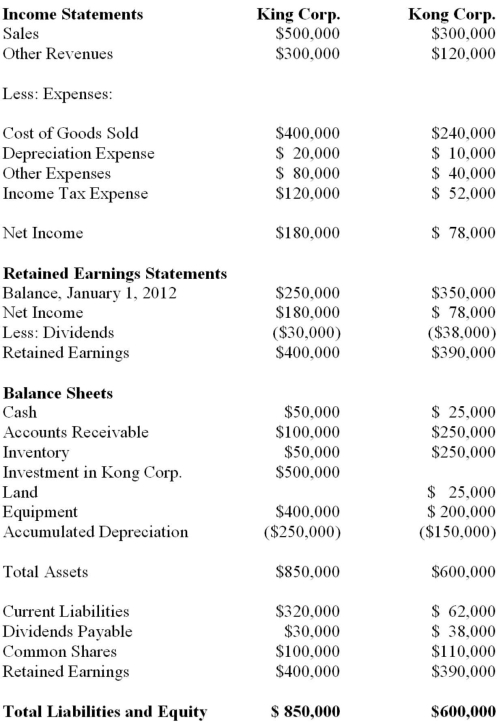 Other Information: ▪King sold a tract of Land to Kong at a profit of $10,000 during 2012. This land is still the property of Kong Corp.
Other Information: ▪King sold a tract of Land to Kong at a profit of $10,000 during 2012. This land is still the property of Kong Corp.
▪On January 1, 2012, Kong sold equipment to King at a price that was $20,000 higher than its book value. The equipment had a remaining useful life of 4 years from that date.
▪On January 1, 2012, King's inventories contained items purchased from Kong for $10,000. This entire inventory was sold to outsiders during the year. Also during 2012, King sold Inventory to Kong for $50,000. Half this inventory is still in Kong's warehouse at year end. All sales are priced at a 25% mark-up above cost, regardless of whether the sales are internal or external.
▪Kong's Retained Earnings on the date of acquisition amounted to $350,000. There have been no changes to the company's common shares account.
▪Kong's book values did not differ materially from its fair values on the date of acquisition with the following exceptions:
▪Inventory had a Fair value that was $20,000 higher than its book value. This inventory was sold to outsiders during 2012.
▪A Patent (which had not previously been accounted for) was identified on the acquisition date with an estimated fair value of $15,000. The patent had an estimated useful life of 3 years.
▪There was a goodwill impairment loss of $4,000 during 2012.
▪Both companies are subject to an effective tax rate of 40%.
▪Both companies use straight line amortization. What is the total amount of unrealized pre-tax profits in inventory at the start of 2013?
Definitions:
Income Tax Rate
The measure at which income is taxed, affecting both companies and individuals.
Straight-Line Depreciation
Straight-line depreciation is a method to allocate the cost of a tangible asset over its useful lifespan evenly, implying an equal expense rate for each year of the asset's use.
After-Tax Discount Rate
The rate of return or discount rate applied to cash flows after accounting for the tax impact, used in net present value calculations.
Incremental Sales
The additional sales generated from a specific marketing campaign, sales activity, or product change, beyond regular expected sales.
Q1: Hot Inc. owns 60% of Cold Inc,
Q9: Any negative goodwill arising on the date
Q19: Dragon Corporation acquired a 7% interest in
Q29: If the Investor sells part of its
Q32: Which of the following is NOT currently
Q34: How should the acquisition cost of a
Q38: Big Guy Inc. purchased 80% of the
Q43: Under which accounting standards is the reporting
Q71: Find the critical t-value that corresponds
Q73: The day-to-day work of management teams will