TABLE 15-1
A certain type of rare gem serves as a status symbol for many of its owners. In theory, for low prices, the demand increases and it decreases as the price of the gem increases. However, experts hypothesize that when the gem is valued at very high prices, the demand increases with price due to the status owners believe they gain in obtaining the gem. Thus, the model proposed to best explain the demand for the gem by its price is the quadratic model:
Y = β₀ + β₁X + β₁X² + ε
where Y = demand (in thousands) and X = retail price per carat.
This model was fit to data collected for a sample of 12 rare gems of this type. A portion of the computer analysis obtained from Microsoft Excel is shown below: 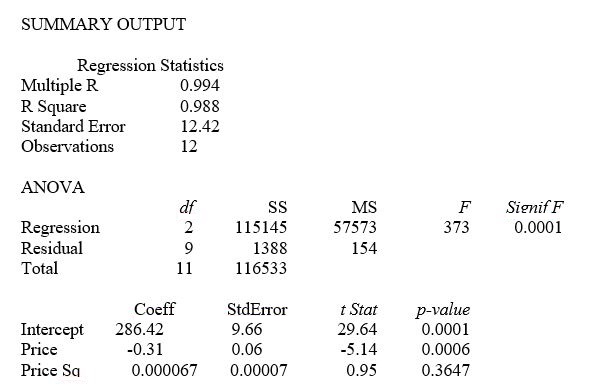
-Referring to Table 15-1, a more parsimonious simple linear model is likely to be statistically superior to the fitted curvilinear for predicting sale price (Y).
Definitions:
Manufacturing Overhead Account
An accounting term that aggregates all indirect costs associated with manufacturing a product.
Adjusting
The process of making modifications to certain accounts through adjusting entries to reflect the true financial status of a business at the end of an accounting period.
Work in Process Inventory
This refers to the materials, labor, and overhead costs for products that are in the production process but not yet completed.
Overapplied Overhead
A situation where the allocated manufacturing overhead cost is more than the actual overhead incurred.
Q22: Referring to Table 14-15, you can conclude
Q51: Referring to Table 16-5, the number of
Q80: The annual multiplicative time-series model does not
Q96: If the Durbin-Watson statistic has a value
Q103: Referring to Table 14-19, what is the
Q115: Referring to Table 17-4, what is the
Q230: Referring to Table 14-3, when the economist
Q246: Referring to Table 14-15, the null hypothesis
Q274: Referring to Table 14-19, which of the
Q293: Referring to Table 14-13, the fitted model