You have isolated five mutations (1 to 5) in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae that make the haploid cells unable to grow in the absence of histidine. Each haploid mutant can be mated with any of the other ones, forming diploid cells that either can (+) or cannot (-) grow in the absence of histidine, as indicated in the following complementation table. How many complementation groups do these mutations represent? Each complementation group typically corresponds to a separate gene. 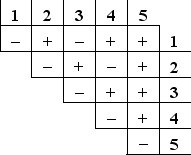
Definitions:
Q2: Indicate true (T) and false (F) statements
Q6: Electron microscopy samples are often chemically fixed
Q7: If the concentration of free subunits is
Q9: What tragic effect of climate change is
Q27: A certain region of a mammalian genome
Q28: Consider two mammalian cells, one in G₁
Q31: Which of the following better describes a
Q33: Five major types of chromatin were identified
Q35: Neuromuscular transmission involves the sequential activation of
Q50: DNA ligases are used in both DNA