The following questions are based on the problem description, regression results, and the RiskSolver Platform (RSP) Discriminant Analysis report below.
A college admissions officer wants to evaluate graduate school applicants based on their GMAT scores, verbal and quantitative. Students are classified as either successful or not-successful in their graduate studies. The officer has data on 20 current students, ten of whom are doing very well (Group 1) and ten who are not (Group 2) .
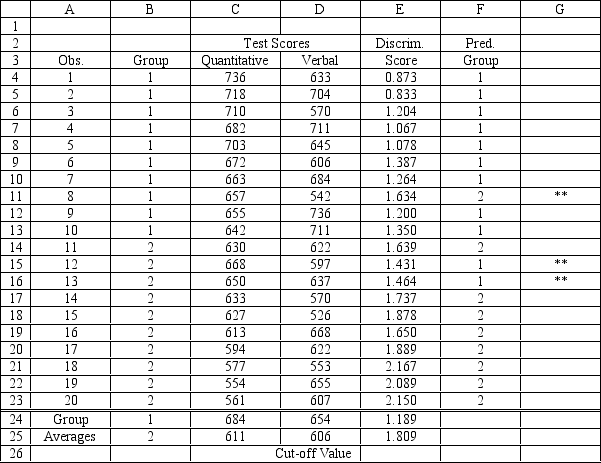
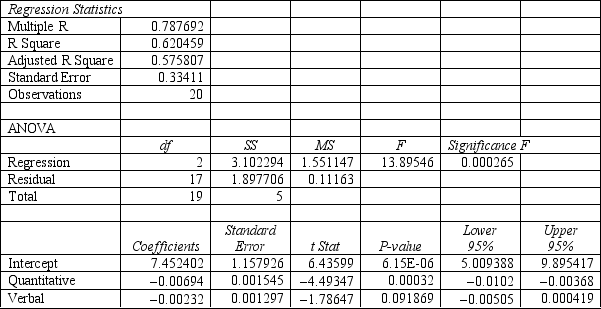
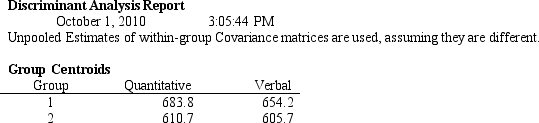

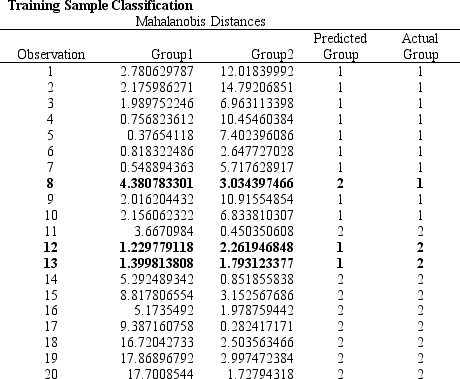
-Refer to Exhibit 10.1. The straight line distance between two points (X1, Y1) and (X2, Y2) is calculated as
Definitions:
Partnership Interest
Represents an individual's or entity's ownership share in a partnership, including rights to its profits and assets.
Capital Account Balance
This term refers to the total amount of funds contributed by investors or owners plus retained earnings in a company's or individual's financial account.
Ownership Interest
An individual's or entity's legal rights and claims to an asset or property, typically reflecting the extent of ownership and stake.
Partnership Capital
The total amount of assets or equity contributed by all partners in a partnership.
Q8: Refer to Exhibit 13.3. What is the
Q11: A parent-subsidiary group is one in which
Q14: Customers arrive at a store randomly, following
Q16: A farmer is planning his spring planting.
Q24: The B & B algorithm solves ILP
Q32: Refer to Exhibit 11.3. Assume the forecasted
Q33: A sub-problem in a B & B
Q88: Corporate tax returns are due 3.5 months
Q95: Refer to Exhibit 11.8. What are
Q105: Refer to Exhibit 11.21. What formulas should