Given the information below,calculate the expected growth rate (g) of dividends,using the constant growth model 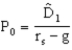 Beta = 1.75;rRF = 7 percent;rM = 11 percent;dividend payout ratio = 30 percent;rd = 10 percent (paid) on all long-term debt;P/E ratio = 10;sales = 5,000 units;sales price per unit = $5;variable cost per unit = $2;fixed cost = $1,000;common stock shares outstanding = 5,000;long-term debt outstanding = $10,000;tax rate = 40 percent.Assume equilibrium exists in the market.
Beta = 1.75;rRF = 7 percent;rM = 11 percent;dividend payout ratio = 30 percent;rd = 10 percent (paid) on all long-term debt;P/E ratio = 10;sales = 5,000 units;sales price per unit = $5;variable cost per unit = $2;fixed cost = $1,000;common stock shares outstanding = 5,000;long-term debt outstanding = $10,000;tax rate = 40 percent.Assume equilibrium exists in the market.
Definitions:
Supply And Demand Graph
A visual representation used in economics to show the relationship between the supply of products and the demand for them.
Public Good
A product or service that is non-excludable and non-rivalrous, meaning it can be used by anyone without diminishing its availability to others.
Allocative Efficiency
The apportionment of resources among firms and industries to obtain the production of the products most wanted by society (consumers); the output of each product at which its marginal cost and marginal benefit are equal, and at which the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus is maximized.
Marginal Costs
The additional cost incurred by producing one more unit of a good or service, crucial for making production and pricing decisions.
Q7: The coefficient of variation is useful in
Q14: Suppose a new company decides to raise
Q25: A company is analyzing two mutually exclusive
Q35: Anderson Company has four investment opportunities with
Q35: According to the signaling theory of capital
Q46: An investor receives a margin call because<br>A)
Q58: Use the information below to solve for
Q73: The Seattle Corporation has been presented with
Q111: The central result from the work of
Q147: A project's market risk rises if the