In Problem 3, Professor Nightsoil's utility function is UN(BN, PN)  and Dean Interface's utility function is UI(BI, PI)
and Dean Interface's utility function is UI(BI, PI) 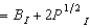 . If Nightsoil's initial endowment is 7 bromides and 5 platitudes and if Interface's initial endowment is 8 bromides and 10 platitudes, then at any Pareto efficient allocation where both persons consume positive amounts of both goods,
. If Nightsoil's initial endowment is 7 bromides and 5 platitudes and if Interface's initial endowment is 8 bromides and 10 platitudes, then at any Pareto efficient allocation where both persons consume positive amounts of both goods,
Definitions:
Reverse Order
A sequence of objects or tasks arranged in the opposite manner from which they were initially presented or executed.
Cost Flow Assumption
An accounting method that determines the value of remaining inventory and the cost of goods sold, such as FIFO or LIFO.
Weighted Average
A calculation that takes into account the varying degrees of importance of the numbers in a data set, assigning weights to some numbers more than others.
Q4: In Problem 1, if demand in the
Q7: (See Problem 4, the Stag Hunt.) Two
Q9: Suppose that Fenner Smith of Problem 2
Q13: Suppose that in New Crankshaft, Pennsylvania, the
Q16: A price-discriminating monopolist sells in two separate
Q16: (See Problem 2.) Willy's only source of
Q16: Recall Bob and Ray in Problem 4.
Q17: Chillingsworth from Problem 10 has a neighbor,
Q29: Bernice in Problem 5 has the utility
Q98: Which one of the following statements is