For the reaction CuS(s)+ H2(g) 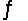 H2S(g)+ Cu(s),
H2S(g)+ Cu(s),
G°f (CuS)= -53.6 kJ/mol
G°f (H2S)= -33.6 kJ/mol
H°f (CuS)= -53.1 kJ/mol
H°f (H2S)= - 20.6 kJ/mol
Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant (Kp)for this reaction at 298 K.
Definitions:
Standard Hours
Refers to the set amount of time expected to perform a specific task or produce a specific quantity of goods.
Direct Labor Rate Variance
The difference between the actual cost of direct labor and the expected (or standard) cost, used in manufacturing cost analysis.
Actual Costs
The real costs incurred in the production of goods or services, as opposed to estimated or forecasted costs.
Standard Costs
Standard costs are predetermined calculations used in cost accounting that represent the expected cost of manufacturing or producing goods under normal conditions.
Q23: Which of these molecules is unsaturated?<br>A)CH<sub>4</sub><br>B)C<sub>2</sub>H<sub>6</sub><br>C)C<sub>4</sub>H<sub>6</sub><br>D)C<sub>5</sub>H<sub>12</sub><br>E)C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>14</sub>
Q29: P<sub>4</sub>O<sub>10</sub> is classified as an acidic oxide
Q31: For the reaction H<sub>2</sub>(g)+ I<sub>2</sub>(g) <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3245/.jpg"
Q32: For the reaction 3H<sub>2</sub>(g)+ N<sub>2</sub>(g) <img
Q38: Which of the following is a catalyst
Q38: Without reference to a table, arrange
Q63: Consider this reaction at equilibrium at a
Q83: In the reaction Ag<sup>+</sup>(aq)+ Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq) <span
Q106: What is the pH at the equivalence
Q108: Determine the equilibrium constant (K<sub>eq</sub>)at 25°C