(Continuation of the Purchasing Power Parity question from Chapter 4)The news-magazine The Economist regularly publishes data on the so called Big Mac index and exchange rates between countries. The data for 30 countries from the April 29, 2000 issue is listed below: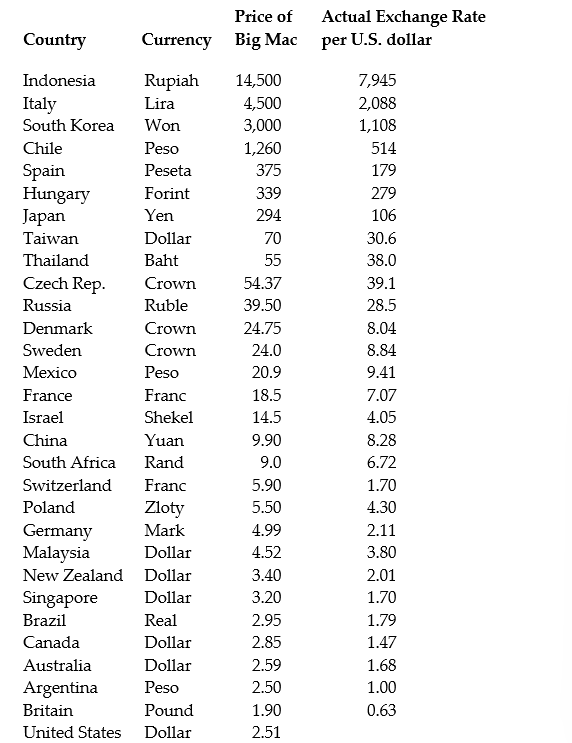
The concept of purchasing power parity or PPP ("the idea that similar foreign and domestic goods … should have the same price in terms of the same currency," Abel, A. and B. Bernanke, Macroeconomics, 4th edition, Boston: Addison Wesley, 476)suggests that the ratio of the Big Mac priced in the local currency to the U.S. dollar price should equal the exchange rate between the two countries.
After entering the data into your spread sheet program, you calculate the predicted exchange rate per U.S. dollar by dividing the price of a Big Mac in local currency by the U.S. price of a Big Mac ($2.51). To test for PPP, you regress the actual exchange rate on the predicted exchange rate.
The estimated regression is as follows: = -27.05 + 1.35 × 1.35×Pr edExRate R2 = 0.994, n = 29, SER = 122.15
(23.74)(0.02)
(a)Your spreadsheet program does not allow you to calculate heteroskedasticity robust standard errors. Instead, the numbers in parenthesis are homoskedasticity only standard errors. State the two null hypothesis under which PPP holds. Should you use a one-tailed or two-tailed alternative hypothesis?
(b)Calculate the two t-statistics.
(c)Using a 5% significance level, what is your decision regarding the null hypothesis given the two t-statistics? What critical values did you use? Are you concerned with the fact that you are testing the two hypothesis sequentially when they are supposed to hold simultaneously?
(d)What assumptions had to be made for you to use Student's t-distribution?
Definitions:
Humanistic Approach
An approach in psychology that emphasizes the study of the whole person, looking at human behavior through the eyes of the person doing the behaving.
Personal Growth
The process of improving oneself through activities that enhance self-awareness, develop talents, and potentially increase quality of life.
Rational Beings
Individuals who are capable of making decisions based on reason and logic rather than on emotion alone.
Rewarded Behaviors
Actions that are encouraged or reinforced through positive outcomes or rewards.
Q1: Your textbook states that when you
Q1: When there are omitted variables in the
Q5: Sports economics typically looks at winning
Q5: Sample selection bias<br>A)occurs when a selection process
Q6: The rule-of-thumb for checking for weak instruments
Q27: Table 8.1 on page 284 of
Q44: Show that the two alternative formulae
Q45: The adjusted R<sup>2</sup>, or <span
Q73: A force-carrying particle is a(n)<br>A)lepton.<br>B)baryon.<br>C)meson.<br>D)intermediate (or gauge)boson.<br>E)hadron.
Q90: Which of the following is not a