You collect monthly data on the money supply (M2)for the United States from 1962:1-2002:4 to forecast future money supply behavior. 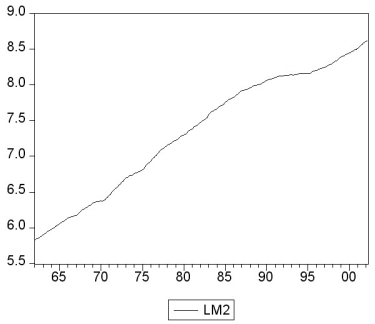
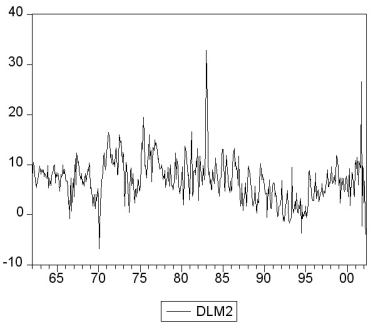 where LM2 and DLM2 are the log level and growth rate of M2.
where LM2 and DLM2 are the log level and growth rate of M2.
(a)Using quarterly data, when analyzing inflation and unemployment in the United States, the textbook converted log levels of variables into growth rates by differencing the log levels, and then multiplying these by 400. Given that you have monthly data, how would you proceed here?
(b)How would you go about testing for a stochastic trend in LM2 and DLM2? Be specific about how to decide the number of lags to be included and whether or not to include a deterministic trend in your test. The textbook found the (quarterly)inflation rate to have a unit root. Does this have any affect on your expectation about whether or not the (monthly)money growth rate should be stationary?
(c)You decide to conduct an ADF unit root test for LM2, DLM2, and the change in the growth rate ΔDLM2. This results in the following t-statistic on the parameter of interest. Find the critical value at the 1%, 5%, and 10% level and decide which of the coefficients is significant. What is the alternative hypothesis?
(d)In forecasting the money growth rate, you add lags of the monetary base growth rate (DLMB)to see if you can improve on the forecasting performance of a chosen AR(10)model in DLM2. You perform a Granger causality test on the 9 lags of DLMB and find a F-statistic of 2.31. Discuss the implications.
(e)Curious about the result in the previous question, you decide to estimate an ADL(10,10)for DLMB and calculate the F-statistic for the Granger causality test on the 9 lag coefficients of DLM2. This turns out to be 0.66. Discuss.
(f)Is there any a priori reason for you to be skeptical of the results? What other tests should you perform?
Definitions:
Supply Chain Manager
A professional role focusing on overseeing and managing a company's supply chain operations to maximize efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure the timely delivery of products.
Production Floor
The area of a manufacturing facility where goods are actually produced or assembled.
Purchase Order
A formal document sent by a buyer to a seller requesting the purchase of products or services, specifying types, quantities, and agreed prices.
Legal Obligation
A duty enforced by law that requires an individual or entity to act or refrain from acting in a certain manner.
Q1: When there are omitted variables in the
Q5: In a Monte Carlo study, econometricians generate
Q10: Consider the regression model Y<sub>i</sub> =
Q27: In the multiple regression model with
Q29: If the causal effect is different for
Q35: "Empirical studies of economic growth are flawed
Q35: Any asset used to make purchases is<br>A)
Q40: The Bayes-Schwarz Information Criterion (BIC)is given
Q84: A banking panic is an episode in
Q101: The money supply in Econland is 1,500,and