The figure below shows revenue and cost curves of a natural monopoly firm.Figure 14.1
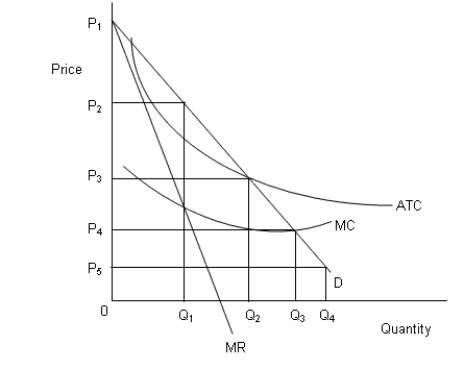 In the figure,
In the figure,
D: Demand curve
MR: Marginal revenue curve
MC: Marginal cost curve
ATC: Average total cost curve
-According to Figure 14.1, in order to attain allocative efficiency, the regulatory body must attempt to set the price equal to:
Definitions:
Ultra Vires
Acts or transactions conducted by a corporation that fall outside the scope of powers and purposes defined by its charter or laws; such acts may be invalid or unauthorized.
Clayton Act
The Clayton Act is a U.S. antitrust law, enacted in 1914, aimed at promoting competition and preventing monopolies by addressing specific practices not covered by the Sherman Act.
Interlocking Directorates
In antitrust law, a situation that occurs when individuals serve as directors for two corporations that are competitors.
Golden Parachute
A substantial financial package granted to a corporate executive upon termination, often after a takeover or merger.
Q7: The existence of externalities in a market
Q22: In contrast to perfect competition, in a
Q50: Which of the following is not a
Q62: The maturity date of a bond is:<br>A)the
Q65: For a perfectly competitive firm, in the
Q66: Consider a perfectly competitive firm that can
Q77: If a profit-maximizing, perfectly competitive firm is
Q88: When a price rise of an asset
Q99: In Table 11.4, assume that total fixed
Q115: Refer to Table 10.1. If the market