In the following figure, the first panel shows a market situation prior to regulation and the second panel shows the effects of regulation.Figure 14.2
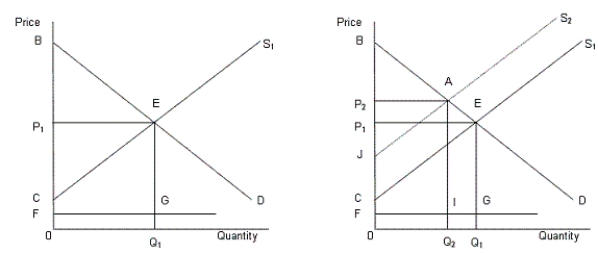 In the figure,
In the figure,
D: Demand curve for automobiles
S1: Supply curve of automobiles prior to regulation
S2: Supply curve of automobiles after regulation
FG: Clean up cost per unit
-Social regulation means that the government dictates the price that a firm must charge and/or the quantity that a firm must supply.
Definitions:
Economies of Scale
Businesses gain cost benefits from increasing their scale of operations, leading to a decline in the cost per unit of output as the production size enlarges.
Q₄
Refers typically to the fourth quarter of a financial year, marking the last segment of the fiscal calendar for businesses and economies.
Economic Profit
The variance between total income and all costs, both seen and unseen, of a company.
Business Shutdown
A temporary or permanent cessation of operations by a firm due to financial difficulties or external circumstances.
Q15: What causes the market supply curve to
Q22: In contrast to perfect competition, in a
Q22: According to Table 13.1, at the social
Q26: A perfectly competitive employer of an input
Q31: Economic theory suggests that the consumer prejudice
Q31: When a negative externality exists in the
Q38: If the P/E ratio is equal to
Q39: The supply curve in the market for
Q58: If 50 percent of the population receives
Q76: Suppose that the demand for apples in