In the following figure, the first panel shows a market situation prior to regulation and the second panel shows the effects of regulation.Figure 14.2
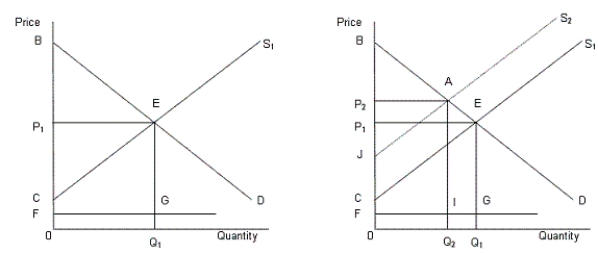 In the figure,
In the figure,
D: Demand curve for automobiles
S1: Supply curve of automobiles prior to regulation
S2: Supply curve of automobiles after regulation
FG: Clean up cost per unit
-When examining the costs of regulation to the U.S. economy, economists can safely ignore the opportunity costs of regulation because they are relatively insignificant compared with the direct costs of regulation.
Definitions:
Comparative Advantage
The proficiency of an entity, whether it's an individual, corporate body, or state, to create a good or offer a service at a more economical opportunity cost than its competition.
Opportunity Cost
The cost of forgoing the next best alternative when making a decision or choosing a particular course of action.
Comparative Advantage
The ability of an individual, firm, or country to produce a good or service at a lower opportunity cost than competitors, leading to more efficient global production patterns.
Specialize
The process of focusing efforts and resources on a narrow area of expertise to increase efficiency and proficiency.
Q1: In the following figure, the first panel
Q23: Which of the following is true of
Q37: Most industrial countries have adopted the regressive
Q56: The table given below states the value
Q81: Which of the following is true of
Q84: When all costs and benefits of a
Q87: When firms use cost-plus pricing in a
Q92: If 81 percent of Canada's exports go
Q128: The table given below reports the value
Q129: The figure given below represents the macroeconomic