You have collected data for 104 countries to address the difficult questions of the determinants for differences in the standard of living among the countries of the world.You recall from your macroeconomics lectures that the neoclassical growth model suggests that output per worker (per capita income)levels are determined by,among others,the saving rate and population growth rate.To test the predictions of this growth model,you run the following regression: 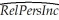 = 0.339 - 12.894 × n + 1.397 × SK,R2=0.621,SER = 0.177
= 0.339 - 12.894 × n + 1.397 × SK,R2=0.621,SER = 0.177
(0.068)(3.177)(0.229)
where RelPersInc is GDP per worker relative to the United States,n is the average population growth rate,1980-1990,and SK is the average investment share of GDP from 1960 to 1990 (remember investment equals saving).Numbers in parentheses are for heteroskedasticity-robust standard errors.
(a)Calculate the t-statistics and test whether or not each of the population parameters are significantly different from zero.
(b)The overall F-statistic for the regression is 79.11.What is the critical value at the 5% and 1% level? What is your decision on the null hypothesis?
(c)You remember that human capital in addition to physical capital also plays a role in determining the standard of living of a country.You therefore collect additional data on the average educational attainment in years for 1985,and add this variable (Educ)to the above regression.This results in the modified regression output: 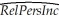 = 0.046 - 5.869 × n + 0.738 × SK + 0.055 × Educ,R2=0.775,SER = 0.1377
= 0.046 - 5.869 × n + 0.738 × SK + 0.055 × Educ,R2=0.775,SER = 0.1377
(0.079)(2.238)(0.294)(0.010)
How has the inclusion of Educ affected your previous results?
(d)Upon checking the regression output,you realize that there are only 86 observations,since data for Educ is not available for all 104 countries in your sample.Do you have to modify some of your statements in (d)?
Definitions:
Australia
A country located in the Southern Hemisphere, known for its unique biodiversity and landmark sites like the Sydney Opera House and the Great Barrier Reef.
Thalamus
A small structure within the brain that serves as a relay station for nerve signals, particularly those related to the senses.
Cerebellum
A region of the brain that plays a vital role in motor control, and is also involved in cognitive functions like attention and language.
Hypothalamus
A region of the brain responsible for producing hormones that control body temperature, hunger, moods, and the release of hormones from other glands.
Q2: Δ2Yt<br>A)= ΔYt - ΔYt-1.<br>B)= <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2833/.jpg" alt="Δ2Yt
Q9: The neoclassical growth model predicts that for
Q11: Model risk can occur when the wrong
Q21: To obtain the slope estimator using the
Q21: The relationship between the spot yield and
Q28: In the linear regression model,Yi = β0
Q42: An equity swap with fixed interest payments
Q44: A contingent-pay option allows the holder to
Q47: The population multiple regression model when there
Q54: The primary problem in pricing electricity derivatives