There are frequently situations where you have information on the conditional distribution of Y given X,but are interested in the conditional distribution of X given Y.Recalling Pr(Y = y 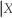 = x)=
= x)= 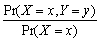 ,derive a relationship between Pr(X = x
,derive a relationship between Pr(X = x 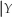 = y)and Pr(Y = y
= y)and Pr(Y = y 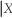 = x).This is called Bayes' theorem.
= x).This is called Bayes' theorem.
Definitions:
Exclusively
Solely or only; limited to a single person, group, category, or purpose without involving others.
Extensive Drought
A prolonged period of abnormally low rainfall, leading to a severe water shortage affecting large geographic areas.
Social Change
The alteration in the social order of a society, which may include changes in nature, social institutions, social behaviors, or social relations.
Demographic Changes
Alterations in the statistical characteristics of a population over time, including age, race, gender distribution, and other factors affecting population dynamics.
Q3: Estimation of the IV regression model<br>A)requires exact
Q3: An estimator is<br>A)an estimate.<br>B)a formula that gives
Q14: The OLS residuals, <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2833/.jpg" alt="The OLS
Q18: In the multiple regression model,the t-statistic for
Q22: Let the vertical axis of a figure
Q24: Your textbook discussed the regression model when
Q33: Consider a situation where Y is related
Q34: The central limit theorem<br>A)states conditions under which
Q38: A pattern in the coefficients of the
Q58: In the case of perfect multicollinearity,OLS is