You have collected quarterly data on inflation and unemployment rates for Canada from 1961:III to 1995:IV to estimate a VAR(4)model of the change in the rate of inflation and the unemployment rate.The results are 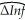 t = 1.02 - .54 ΔInft-1 - .46 ΔInft-2 - .32 ΔInft-2 - .01 ΔInft-4
t = 1.02 - .54 ΔInft-1 - .46 ΔInft-2 - .32 ΔInft-2 - .01 ΔInft-4
.09)(.09)(.09)(.08)(.44)
-.76 Unempt-1 + .20 Unempt-2 - .16 Unempt-3 + .59 Unempt-4
(.43)(.76)(.76)(.44) 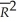 = .26.
= .26. 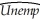 t = 0.18 - .003 ΔInft-1 - .016 ΔInft-2 - .018 ΔInft-3 - .010 ΔInft-4
t = 0.18 - .003 ΔInft-1 - .016 ΔInft-2 - .018 ΔInft-3 - .010 ΔInft-4
(.10)(.016)(.018)(.017)(.016)
+ 1.47 Unempt-1 - .46 Unempt-2 - .08 Unempt-3 + .05 Unempt-4
(.08)(.14)(.14)(.08) 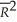 = .980.
= .980.
(a)Explain how you would use the above regressions to conduct one period ahead forecasts.
(b)Should you test for cointegration between the change in the inflation rate and the unemployment rate and,in the case of finding cointegration here,respecify the above model as a VECM?
(c)The Granger causality test yields the following F-statistics: 3.75 for the test that the coefficients on lagged unemployment rate in the change of inflation equation are all zero;and 0.36 for the test that the coefficients on lagged changes in the inflation rate are all zero.Based on these results,does unemployment Granger-cause inflation? Does inflation Granger-cause unemployment?
Definitions:
Phineas Gage
A railroad worker from the 19th century whose behavioral changes after surviving a severe brain injury contributed to the understanding of the role of the frontal lobes in personality.
Limited Emotions
A condition or state where an individual experiences a reduced range of emotions, often due to psychological or neurological factors.
Emotional Intelligence
The skill to comprehend, regulate, and communicate one's emotional state, alongside the capability to manage social interactions with discretion and empathy.
Decision Making
The cognitive process of selecting a course of action from among multiple alternatives, often involving considerations of risk, benefit, and personal values.
Q4: The distributed lag model relating orange juice
Q15: The power of the test is<br>A)dependent on
Q21: You recall from one of your earlier
Q29: Females,on average,are shorter and weigh less than
Q29: Write a short essay about the Overidentifying
Q31: The error term in a multiperiod regression<br>A)is
Q41: You have collected quarterly data on inflation
Q45: The neoclassical growth model predicts that for
Q53: Consider the following multiple regression models (a)to
Q84: A study was performed to examine the