You are hired to forecast the unemployment rate in a geographical area that is peripheral to a large metropolitan area in the United States.The area in question is called the Inland Empire (San Bernardino County and Riverside County)and is situated east of Greater Los Angeles (Los Angeles County and Orange County).While the area has a large population (it is the 14th largest metropolitan statistical area in the United States),its economic activity relies heavily on that of the larger area it is attached to.For example,it is estimated that approximately 20% of its workforce commutes into the Greater Los Angeles area for work and few workers commute the other way.Furthermore,its logistics industry is heavily dependent on economic activity in the Greater Los Angeles Area.As a result,you view the unemployment rate of the Greater Los Angeles Area (urGLA)to be exogenous in determining the unemployment rate in the Inland Empire (urIE).You estimate the following distributed lag model,where numbers in parenthesis are HAC standard errors:
Δ 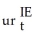 = 0.00002 + 0.74 Δ
= 0.00002 + 0.74 Δ 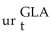 - 0.04 Δ
- 0.04 Δ 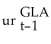 - 0.01 Δ
- 0.01 Δ 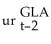 + 0.07 Δ
+ 0.07 Δ 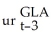 + 0.05 Δ
+ 0.05 Δ 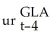 (0.00010)(0.06)(0.06)(0.06)(0.06)(0.06)
(0.00010)(0.06)(0.06)(0.06)(0.06)(0.06)
+ 0.09 Δ 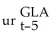 + 0.10Δ
+ 0.10Δ 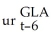 (0.05)(0.06)
(0.05)(0.06)
t = 1991:01-2009:12,R2 = 0.60,SER = 0.001
a.What is the impact effect of a one percentage point increase (say from 0.06 to 0.07)of the unemployment rate in the Greater Los Angeles area?
b.What is the long-run cumulative dynamic multiplier?
c.Why do you think the variables above appear in changes rather than in levels?
Definitions:
Gender Stereotyping
The practice of ascribing to an individual specific attributes, characteristics, or roles by reason only of their gender.
Gender Constancy
The understanding that one's gender remains the same across time and situations, typically developed by age 6 or 7.
Gender Stability
The understanding and recognition that one's gender identity is consistent and persistent over time.
Electra Complex
A psychoanalytic concept referring to a girl's psychosexual competition with her mother for possession of her father.
Q13: In the process of collecting weight and
Q13: The error term is homoskedastic if<br>A)var(ui <img
Q18: The logit regression (11.10)on page 393 of
Q22: Your textbook so far considered variables for
Q28: It is estimated that 780,000 surgical site
Q40: Failure to follow the treatment protocol means
Q42: The cost of attending your college has
Q46: Your textbook suggests an "entity-demeaned" procedure to
Q48: A vector autoregression<br>A)is the ADL model with
Q109: The Poisson distribution is a discrete distribution