The Poisson distribution is a discrete distribution that expresses the probability of a fixed number of events occurring in a fixed interval.For example,suppose we want to model the number of arrivals per minute at the campus dining hall during lunch.We observe the actual arrivals in 200 one-minute periods in 1 week.The sample mean is 3.8 and the results are shown below. 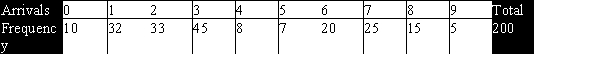 The probabilities based on a Poisson distribution with a mean of 3.8 are shown below.
The probabilities based on a Poisson distribution with a mean of 3.8 are shown below. 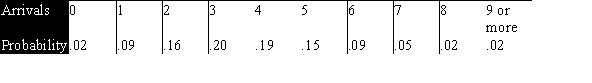 What is the expected count for 0 arrivals?
What is the expected count for 0 arrivals?
Definitions:
Radiolaria
Microscopic planktonic marine organisms with intricate silica skeletons, important in paleoclimate studies.
Trypanosomes
Single-celled parasitic protozoans, known for causing diseases like sleeping sickness in humans and animals.
Infect
The process by which organisms, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites, enter, invade, and multiply within another organism, causing disease or illness.
Biting Insects
Biting insects are those that pierce the skin of humans or animals to feed on blood; common examples include mosquitoes, flies, and ticks, which can also act as vectors for various diseases.
Q7: When you add state fixed effects to
Q13: Suppose you have two math classes (math
Q30: When testing joint hypothesis,you can use<br>A)the F-
Q32: You want to study the relationship between
Q34: You are interested in determining if the
Q38: The Hawthorne effect refers to<br>A)subjects dropping out
Q39: Two authors published a study in 1992
Q45: Suppose we have two binomial populations where
Q47: A causal effect for a single individual<br>A)can
Q72: The length of time it takes to