To enter the host cell, intracellular bacterial pathogens can induce phagocytosis in cells that are normally nonphagocytic. This is done by two major mechanisms depicted in the following schematic diagrams (A and B). Indicate whether each of the following descriptions better applies to mechanism A or B. Your answer would be a four-letter string composed of letters A and B only, e.g. ABAA.
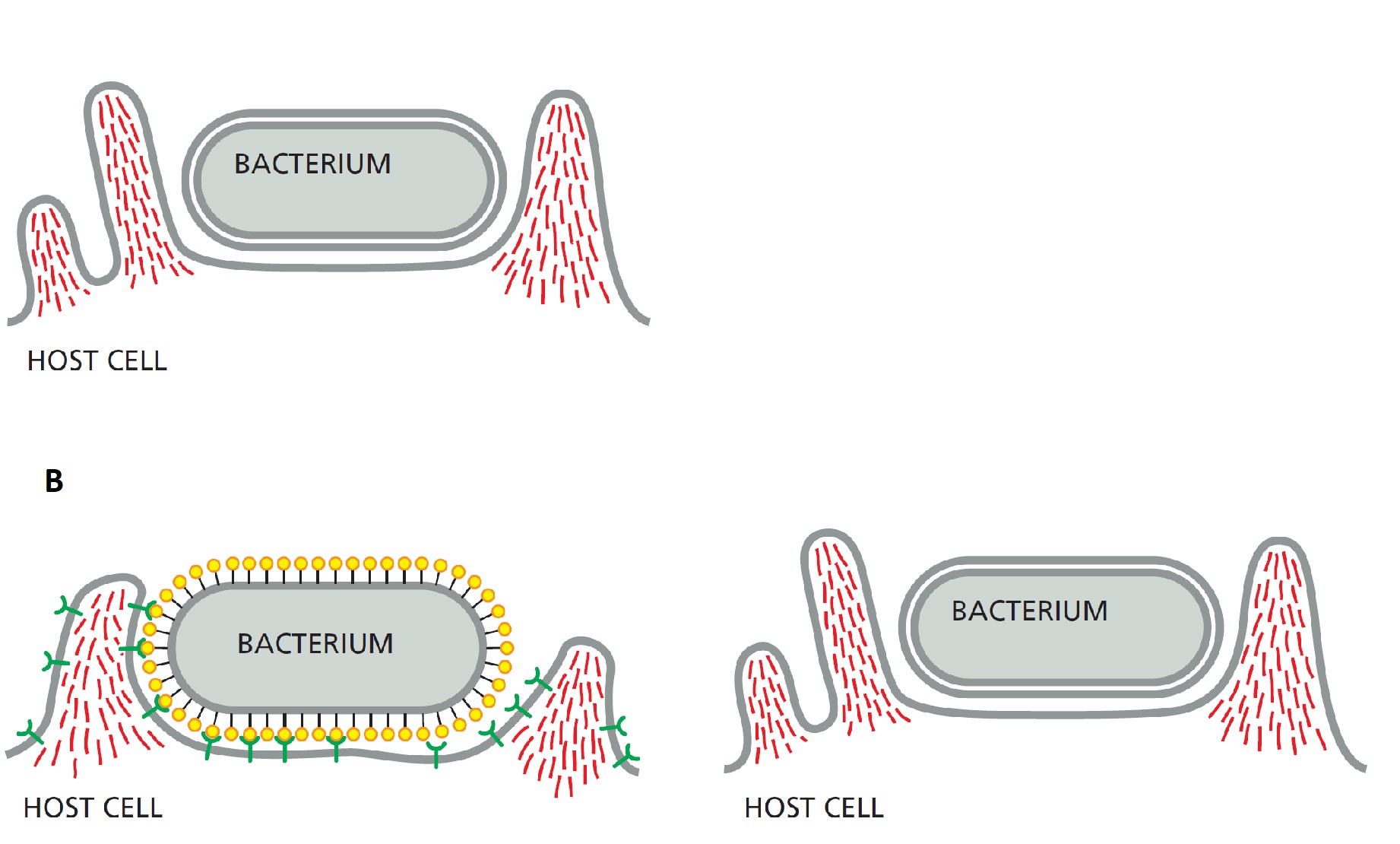
( ) It is called the zipper mechanism.
( ) It depends on invasin proteins on the surface of the bacterium that bind to their receptors on the surface of the host cell.
( ) It depends on the injection of effector proteins into the host cell by a bacterial secretion system.
( ) It resembles the process of macropinocytosis.
Definitions:
Economic Losses
Financial deficits incurred by businesses, individuals, or governments due to economic downturns or adverse market conditions.
Marginal Cost
The change in total cost that arises when the quantity produced is incremented by one unit; essentially, the cost of producing one additional unit of a good.
Standby Customers
Customers who are available to purchase or subscribe to a service on an as-needed basis, often used in context with utilities or telecommunications.
Profit
The financial gain obtained when the revenue earned from business activities exceeds the expenses, costs, and taxes involved in sustaining the activity.
Q5: Food-drug interactions have the potential to cause
Q8: Apoptotic cells are efficiently phagocytosed by neighboring
Q9: Indispensable amino acids are essential for the
Q12: Each is a function of the liver,except
Q15: In which situation is fluoridated drinking water
Q19: Indicate if each of the following descriptions
Q24: Sort the following events into the order
Q25: Indicate whether each of the following descriptions
Q33: Indicate whether each of the following descriptions
Q38: Imagine a morphogen gradient established from left