To examine the differences between salaries of male and female middle managers of a large bank, 90 individuals were randomly selected, and two models were created with the following variables considered: Salary = the monthly salary (excluding fringe benefits and bonuses) ,
Educ = the number of years of education,
Exper = the number of months of experience,
Train = the number of weeks of training,
Gender = the gender of an individual; 1 for males, and 0 for females.
Excel partial outputs corresponding to these models are available and shown below.
Model A: Salary = β0 + β1Educ + β2Exper + β3Train + β4Gender + ε 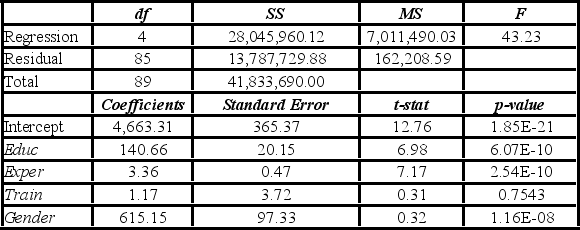 Model B: Salary = β0 + β1Educ + β2Exper + β3Gender + ε
Model B: Salary = β0 + β1Educ + β2Exper + β3Gender + ε 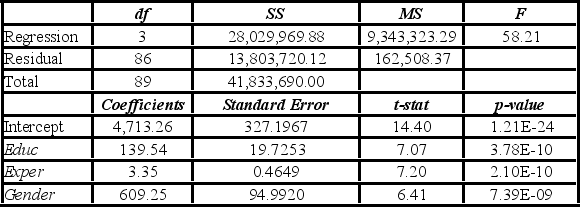 Assuming the same years of education and months of experience, what is the null hypothesis for testing whether the mean salary of males is greater than the mean salary of females using Model B?
Assuming the same years of education and months of experience, what is the null hypothesis for testing whether the mean salary of males is greater than the mean salary of females using Model B?
Definitions:
Menarche
Establishment of menstrual function; the time of the first menstrual period or flow.
Menstrual Bleeding
The monthly shedding of the lining of the uterus (endometrium) when pregnancy does not occur, resulting in bleeding from the vagina.
Sexual Drive
The overall sex drive or desire for sexual activity, influenced by biological, psychological, and social factors.
Menstrual Cycle
Series of changes that occur in sexually mature, nonpregnant women and result in menses. Specifically refers to the uterine cycle but is often used to include both the uterine and ovarian cycles.
Q27: Pfizer Inc. is the world's largest research-based
Q34: In the sample regression equation <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6618/.jpg"
Q35: A portfolio manager is interested in reducing
Q42: Which of the following is the sample
Q64: For the exponential model ln(y) = β<sub>0</sub>
Q64: The accompanying table shows the regression results
Q87: A trading magazine wants to determine the
Q101: The following table shows the annual revenues
Q112: The only income the option seller can
Q114: For the linear probability model y =