When estimating 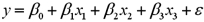 ,you wish to test
,you wish to test 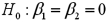 versus
versus 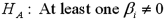 .The value of the test statistic is
.The value of the test statistic is 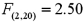 and its associated p-value is 0.1073.At the 5% significance level,the conclusion is to:
and its associated p-value is 0.1073.At the 5% significance level,the conclusion is to:
Definitions:
Calm Down
A phrase used to encourage someone to become less agitated or excited, often aiming to reduce stress or anger.
Therapeutic Technique
A specific process or intervention used in therapy to help individuals cope with or overcome psychological, emotional, or behavioral issues.
Psychotherapist
A professionally trained individual who uses psychological methods and techniques to help people manage and overcome mental health issues, emotional challenges, and personal problems.
Catharsis Hypothesis
The idea that expressing or venting emotions allows an individual to release negative feelings and achieve a state of psychological well-being.
Q5: Exhibit 20.9.A shipping company believes there is
Q20: If s<sup>2</sup> is computed from a random
Q38: Exhibit 15-1.An marketing analyst wants to examine
Q77: When the data is available on x
Q82: Which of the following factors refers to
Q86: Exhibit 17.8.A realtor wants to predict and
Q90: A crucial assumption in a regression model
Q95: Exhibit 16.6.Thirty employed single individuals were randomly
Q109: Exhibit 17.9.A bank manager is interested in
Q110: Exhibit 15-2.A sports analyst wants to exam