(See Problem 11.) Lawrence's expected utility function is 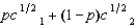 , where p is the probability that he consumes c1 and 1 - p is the probability that he consumes c2. Lawrence is offered a choice between getting a sure payment of $Z or a lottery in which he receives $400 with probability .30 or $2,500 with probability .70. Lawrence will choose the sure payment if
, where p is the probability that he consumes c1 and 1 - p is the probability that he consumes c2. Lawrence is offered a choice between getting a sure payment of $Z or a lottery in which he receives $400 with probability .30 or $2,500 with probability .70. Lawrence will choose the sure payment if
Definitions:
Ruler
A tool in many software applications that provides a visual guide for aligning text, images, and other elements within a document.
Border from Paragraph
A style option that adds a visible outline around a paragraph's text in a document.
No Border Button
A tool in software applications used to remove the border from a selected object or table cell.
Borders Gallery
A collection of border styles and options available in some software applications, enabling users to customize and apply borders to objects or text within documents.
Q12: Suppose that Paul and David from Problem
Q13: Al and Bill are the only workers
Q15: In Problem 9, suppose that Irma's production
Q16: A price-discriminating monopolist sells in two separate
Q17: Remember Bonnie and Clyde from your workbook?
Q25: Economists define public goods to be those
Q27: In Problem 4, Murphy used to consume
Q29: In Problem 4, suppose that the market
Q37: A trade between two people is an
Q41: Suppose that in Horsehead, Massachusetts, the cost