In the 1980s, a mutant strain of mice was identified, carrying amino acid changes in the MHC class II gene. This mutant strain was derived from C57Bl/6 mice, which carry the H-2b haplotype. Inbred H-2b mice express only one MHC class II protein, called Ab. The mutant strain, called 'bm12' was found to have 3 amino acid changes in the Ab protein, at positions 67, 70, and 71 of the Aβ chain. The positions of these amino acid changes on the MHC class II structure are shown below by the red circles in Figure . On the right, the side view diagram of MHC class II shows the direction of these three amino acid side chains. 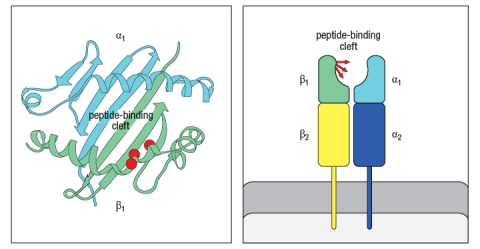
Initial experiments with wild-type C57Bl/6 mice and bm12 mice showed that the wild-type mice made a robust CD4 T cell response after immunization with the insulin protein isolated from a cow; in contrast, the bm12 mice failed to make any detectable response to this foreign protein. Epitope mapping studies identified amino acid residues 1–14 of the bovine insulin A chain as the peptide recognized by CD4 T cells from wild-type mice.
a) What is the most likely explanation for the failure of bm12 mice to make a CD4 T cell response to bovine insulin?
In a second set of experiments, T cells from wild-type (WT) or bm12 mice were mixed in vitro with antigen-presenting cells (APCs), in the presence or absence of the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB), and T cell proliferation was measured. The data from these experiments are shown in Figure. 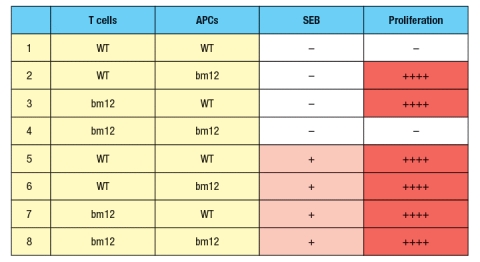
b) What is the explanation for the results in Rows 1–4 of the table?
c) Why does the T cell response to SEB (Rows 5–8) show a different pattern than the response to bovine insulin?
d) In the table above, T cell proliferation was measured after 4 days of incubation of T cells, APCs, +/- SEB. If one isolated the T cells at the end of the incubation for the six conditions in which robust proliferation was seen (Rows 2, 3, 5-8), and stained the T cells with each antibody (separately) from a panel of antibodies that recognize each of the mouse V domains (i.e., an antibody to V 1, an antibody to V 2, etc), what result would be expected?
Definitions:
Restriction Enzymes
Proteins used in molecular biology that cut DNA at specific recognition nucleotide sequences, important in genetic engineering.
Bacteriophage Infections
Refers to the invasion and proliferation of bacteriophages, which are viruses that infect bacteria, often leading to the lysis (destruction) of the bacteria cell.
Foreign RNA
RNA that originates from a source other than the host organism, often referring to viral RNA or artificially introduced RNA.
Reverse Transcriptase
An enzyme used by some viruses to synthesize DNA from an RNA template, a critical component of the replication process of retroviruses.
Q2: Genetic studies have identified more than 40
Q5: Variable Ig domain<br>
Q6: When vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) is used
Q7: Individuals with defects in ubiquitously expressed DNA
Q10: Nearly 80% of patients with autoimmune
Q14: Self-reactive B cells can be eliminated from
Q16: Unlike somatic hypermutation, class switching occurs in
Q16: All-trans retinoic acid (tRA) is a metabolite
Q25: When mice are born, their intestinal lamina
Q79: i. The base period for one index